
In terms of our original question then, the probability of our random variable returning less than (or equal to) 5.0 is 91.15% and, consequently, the probability of returning greater than 5.0 is 8.85% = 100% – 91.15%.

The total area must be 100% because this is a probability distribution. Put another way, and still referring to the plot on the left above, the probability of a standard random normal variable (again, that’s a normal variable with mean of zero and unit standard deviation) resulting in 1.35 or less is about 91.15%, which is the area under the curve to the left of Z(1.35). What does our 91.15% mean? It is the area under the curve to the left of Z(1.35), see graph on the left: The values inside the Z value table are probabilities, so they must lie between 0% and 100% inclusive. The first function says “The probability that X is less than or equal to 5.0 conditional on a mean of X equal to 2.3 and standard deviation of X equal to 2.0.” The second function, Pr(Z ≤ 1.350), reflects the normalization (translation) from the normal X to the standard normal Z, and we don’t need to specify the mean or standard deviation of the Z.

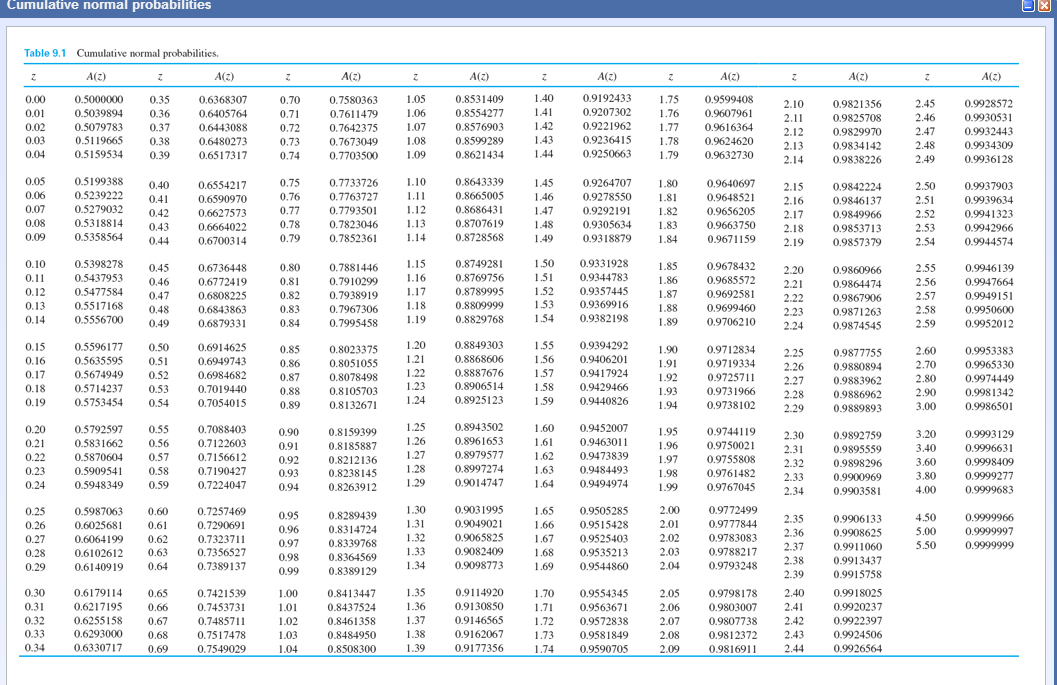
Let’s formalize our answer with some notation: We see here that for Z = 1.35, the probability is 0.9115 or 91.15%. Because our Z-value is 1.35, we want to go down the rows until we arrive at 1.3, then we want to go across the columns until we arrive at 0.05. Below is a typical cumulative Z-value lookup. The Z value of 1.350 means “The value of 5.0 is 1.350 standard deviations above the mean of 2.30.” Now we can use the common Z table to retrieve the associated probability. A standard normal variable has zero mean and variance of one (consequently its standard deviation is also one). The first step is to standardize the given value of 5.0 into a Z value (aka, Z score):Īll we’ve done here is translate a normal variable into a standard normal variable. Parsimony here refers to the normal conveniently has only two parameters, mean and variance. The normal distribution is rarely realistic, but it is popular for learning purposes due to its special properties and what is called parsimony.
I hope you noticed the phrase “normally distributed?” It comes up often in exams. Here is same question re-phrased: If an asset’s daily return is normally distributed with mean of 2.30% and daily volatility of 2.00%, what is the probability the asset’s return will be at least 5.0%? The same question could be re-phrased into the language of asset returns.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
